The Biden administration's efforts to restrict Chinese cars and batteries from entering the U.S. market highlight a complex challenge: balancing national security, economic interests, and climate goals. Here's why this situation is significant and why China is currently leading in the global electric vehicle (EV) race.
1. China's Dominance in the EV Industry
Battery Production: China is the world’s largest producer of batteries, which are the most critical and expensive component of electric vehicles. Companies like CATL and BYD dominate the global market, supplying not only Chinese automakers but also major international brands.
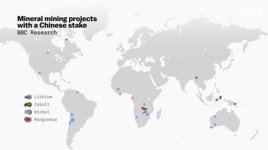
Supply Chain Control: China controls much of the global supply chain for key battery materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. This gives China a significant advantage in the production and cost efficiency of EV batteries.
Government Support: The Chinese government has aggressively supported the EV industry through subsidies, research and development funding, and infrastructure investments, such as charging stations. This has spurred rapid growth in domestic EV companies and made China a global leader in the field.
2. The U.S. Dilemma
Dependence on Chinese Batteries: Despite efforts to develop domestic battery manufacturing, the U.S. remains heavily dependent on Chinese batteries and materials. This reliance makes it challenging for the U.S. to meet its EV production goals without Chinese imports.
Economic and National Security Concerns: The Biden administration's push to keep Chinese EVs and batteries out of the U.S. is partly driven by concerns over economic dependency and national security. There is a fear that allowing Chinese dominance in this critical industry could undermine U.S. economic sovereignty and security interests.
Climate Goals at Risk: The U.S. has set ambitious climate goals, including a significant increase in EV adoption to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, restricting Chinese imports could slow down the transition to EVs by making them more expensive or less available, potentially hindering progress toward these goals.
3. Why China is Winning the EV War
Scale and Cost Efficiency: China's scale in EV production and battery manufacturing allows it to produce these products at a lower cost, giving Chinese companies a competitive edge in both domestic and international markets.
Innovation and Technology: Chinese companies have been at the forefront of EV innovation, developing advanced technologies and expanding their global influence through strategic partnerships and investments.
Global Market Expansion: Chinese EV makers, such as BYD, Nio, and Xpeng, are increasingly expanding into international markets, including Europe and Asia. This global reach further solidifies China's position as a leader in the EV industry.
4. Impact on the U.S. Market
Challenges for U.S. Automakers: U.S. automakers are racing to catch up, but they face challenges in scaling production and securing supply chains for batteries and raw materials without relying on China. This could slow down the availability of affordable EVs in the U.S.
Potential for a Trade-Off: The U.S. may need to balance its goals of protecting domestic industries and reducing dependence on China with the need to meet its climate targets. This could involve tough decisions about tariffs, subsidies, and international cooperation.
5. The Path Forward
Boosting Domestic Production: The U.S. is working to increase domestic production of batteries and EVs through investments in manufacturing, research, and workforce development. This includes initiatives like the Inflation Reduction Act, which incentivizes domestic EV production.
International Partnerships: The U.S. might also look to diversify its supply chains by partnering with other countries, such as those in Europe, to reduce reliance on China while still advancing its EV goals.
Long-Term Strategy: Ultimately, the U.S. needs a long-term strategy that balances the urgency of climate action with the realities of global economic competition. This may involve difficult compromises but is essential for ensuring both national security and environmental sustainability.
In summary, while the Biden administration's stance on Chinese EVs and batteries is driven by legitimate concerns, it also places the U.S. in a challenging position when it comes to meeting its climate goals. China's dominance in the EV industry is a testament to its strategic planning and investment, which has given it a significant lead in the global race to electrify transportation.
Youtube
1. China's Dominance in the EV Industry
Battery Production: China is the world’s largest producer of batteries, which are the most critical and expensive component of electric vehicles. Companies like CATL and BYD dominate the global market, supplying not only Chinese automakers but also major international brands.
Supply Chain Control: China controls much of the global supply chain for key battery materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. This gives China a significant advantage in the production and cost efficiency of EV batteries.
Government Support: The Chinese government has aggressively supported the EV industry through subsidies, research and development funding, and infrastructure investments, such as charging stations. This has spurred rapid growth in domestic EV companies and made China a global leader in the field.

2. The U.S. Dilemma
Dependence on Chinese Batteries: Despite efforts to develop domestic battery manufacturing, the U.S. remains heavily dependent on Chinese batteries and materials. This reliance makes it challenging for the U.S. to meet its EV production goals without Chinese imports.
Economic and National Security Concerns: The Biden administration's push to keep Chinese EVs and batteries out of the U.S. is partly driven by concerns over economic dependency and national security. There is a fear that allowing Chinese dominance in this critical industry could undermine U.S. economic sovereignty and security interests.
Climate Goals at Risk: The U.S. has set ambitious climate goals, including a significant increase in EV adoption to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. However, restricting Chinese imports could slow down the transition to EVs by making them more expensive or less available, potentially hindering progress toward these goals.
3. Why China is Winning the EV War
Scale and Cost Efficiency: China's scale in EV production and battery manufacturing allows it to produce these products at a lower cost, giving Chinese companies a competitive edge in both domestic and international markets.
Innovation and Technology: Chinese companies have been at the forefront of EV innovation, developing advanced technologies and expanding their global influence through strategic partnerships and investments.
Global Market Expansion: Chinese EV makers, such as BYD, Nio, and Xpeng, are increasingly expanding into international markets, including Europe and Asia. This global reach further solidifies China's position as a leader in the EV industry.
4. Impact on the U.S. Market
Challenges for U.S. Automakers: U.S. automakers are racing to catch up, but they face challenges in scaling production and securing supply chains for batteries and raw materials without relying on China. This could slow down the availability of affordable EVs in the U.S.
Potential for a Trade-Off: The U.S. may need to balance its goals of protecting domestic industries and reducing dependence on China with the need to meet its climate targets. This could involve tough decisions about tariffs, subsidies, and international cooperation.
5. The Path Forward
Boosting Domestic Production: The U.S. is working to increase domestic production of batteries and EVs through investments in manufacturing, research, and workforce development. This includes initiatives like the Inflation Reduction Act, which incentivizes domestic EV production.
International Partnerships: The U.S. might also look to diversify its supply chains by partnering with other countries, such as those in Europe, to reduce reliance on China while still advancing its EV goals.
Long-Term Strategy: Ultimately, the U.S. needs a long-term strategy that balances the urgency of climate action with the realities of global economic competition. This may involve difficult compromises but is essential for ensuring both national security and environmental sustainability.
In summary, while the Biden administration's stance on Chinese EVs and batteries is driven by legitimate concerns, it also places the U.S. in a challenging position when it comes to meeting its climate goals. China's dominance in the EV industry is a testament to its strategic planning and investment, which has given it a significant lead in the global race to electrify transportation.
Youtube
