Choosing between an Electric Vehicle (EV), a Plug-In Hybrid (PHEV), or a Hybrid in 2024 depends on various factors such as driving habits, budget, and long-term expectations. Here’s a comparison of the three types, with a focus on Toyota and Tesla models, based on the factors you asked about:
1. Size, Width, Height, Belly Height, Differences
Specification EV (e.g., Tesla Model 3) PHEV (e.g., Toyota RAV4 Prime) Hybrid (e.g., Toyota Camry Hybrid)
Length 184.8 in (Tesla Model 3) 180.9 in (RAV4 Prime) 192.7 in (Camry Hybrid)
Width 72.8 in 73.4 in 72.4 in
Height 56.8 in 68.6 in 56.9 in
Ground Clearance 5.5 in 8.1 in 5.7 in
EVs (like Tesla Model 3) tend to have a low center of gravity for performance and aerodynamics.
PHEVs such as the Toyota RAV4 Prime offer more SUV-like dimensions with higher ground clearance.
Hybrids like the Toyota Camry Hybrid maintain traditional sedan dimensions with moderate height and ground clearance.
2. Fuel/Energy Consumption
Specification EV (Tesla Model 3) PHEV (Toyota RAV4 Prime) Hybrid (Toyota Camry Hybrid)
Fuel Economy (MPGe) 132 MPGe (city) / 128 MPGe (highway) 94 MPGe combined (electric mode) / 38 MPG (gas mode) 51 MPG (city) / 53 MPG (highway)
Electric-Only Range 272-358 miles (Tesla Model 3) 42 miles electric range N/A (only assisted electric)
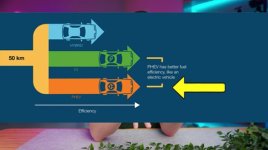
EVs like the Tesla are much more efficient with energy use compared to PHEVs or Hybrids but rely entirely on charging.
PHEVs have both an electric range (around 40-50 miles) and a gasoline backup, offering more flexibility.
Hybrids are the most efficient with gas but have no significant electric-only range.
3. Battery & Range
Specification EV (Tesla Model 3) PHEV (Toyota RAV4 Prime) Hybrid (Toyota Camry Hybrid)
Battery Size 60-82 kWh (Tesla Model 3) 18.1 kWh 1.6 kWh
Range (combined) 272-358 miles 600+ miles (total with gas) 680 miles
EVs have significantly larger batteries, providing extended electric-only range but require charging infrastructure.
PHEVs offer a smaller electric range but combine the benefits of a battery and traditional fuel for long-distance travel.
Hybrids rely on small batteries for short bursts of electric assistance, with no substantial electric-only range.
4. Maintenance Cost/Year
Specification EV (Tesla Model 3) PHEV (Toyota RAV4 Prime) Hybrid (Toyota Camry Hybrid)
Estimated Annual Maintenance Cost $400-$600 $500-$700 $450-$600
EVs have lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts (no engine oil changes, fewer fluids, less brake wear).
PHEVs have moderately higher maintenance costs due to the complexity of both electric and gasoline systems.
Hybrids are generally less expensive than PHEVs but more than EVs due to their reliance on gasoline engines.
5. Trunk Size
Specification EV (Tesla Model 3) PHEV (Toyota RAV4 Prime) Hybrid (Toyota Camry Hybrid)
Trunk Space 15 cu ft (plus front trunk) 33.5 cu ft 15.1 cu ft
Max Cargo Space 22.9 cu ft (w/ rear seats folded) 63.2 cu ft N/A
EVs often benefit from having both a front and rear trunk (as in Tesla models).
PHEVs, especially SUVs like the RAV4 Prime, offer more cargo capacity than hybrids or sedans.
Hybrids offer similar trunk space to their gas-powered counterparts.
6. Defects/Type Issues
EVs (Tesla):
Tesla vehicles have experienced build quality issues in earlier models, including panel gaps and paint quality concerns. However, Tesla’s software and battery systems are generally reliable.
PHEVs (Toyota):
Toyota RAV4 Prime has few major issues but may experience software glitches related to the transition between electric and gasoline modes.
Hybrids (Toyota):
Toyota hybrids like the Camry Hybrid have a long-standing reputation for reliability. However, minor issues such as infotainment bugs have been reported.
Conclusion:
EVs (e.g., Tesla Model 3) are best for those who can rely on charging infrastructure and prefer lower running costs with a focus on eco-friendly driving.
PHEVs (e.g., Toyota RAV4 Prime) offer the best of both worlds, with electric-only driving for short trips and gasoline for longer journeys, making them more versatile.
Hybrids (e.g., Toyota Camry Hybrid) are ideal if you want high fuel efficiency without the need for charging, offering a balance between cost, reliability, and convenience.
Youtube
1. Size, Width, Height, Belly Height, Differences
Specification EV (e.g., Tesla Model 3) PHEV (e.g., Toyota RAV4 Prime) Hybrid (e.g., Toyota Camry Hybrid)
Length 184.8 in (Tesla Model 3) 180.9 in (RAV4 Prime) 192.7 in (Camry Hybrid)
Width 72.8 in 73.4 in 72.4 in
Height 56.8 in 68.6 in 56.9 in
Ground Clearance 5.5 in 8.1 in 5.7 in
EVs (like Tesla Model 3) tend to have a low center of gravity for performance and aerodynamics.
PHEVs such as the Toyota RAV4 Prime offer more SUV-like dimensions with higher ground clearance.
Hybrids like the Toyota Camry Hybrid maintain traditional sedan dimensions with moderate height and ground clearance.

2. Fuel/Energy Consumption
Specification EV (Tesla Model 3) PHEV (Toyota RAV4 Prime) Hybrid (Toyota Camry Hybrid)
Fuel Economy (MPGe) 132 MPGe (city) / 128 MPGe (highway) 94 MPGe combined (electric mode) / 38 MPG (gas mode) 51 MPG (city) / 53 MPG (highway)
Electric-Only Range 272-358 miles (Tesla Model 3) 42 miles electric range N/A (only assisted electric)
EVs like the Tesla are much more efficient with energy use compared to PHEVs or Hybrids but rely entirely on charging.
PHEVs have both an electric range (around 40-50 miles) and a gasoline backup, offering more flexibility.
Hybrids are the most efficient with gas but have no significant electric-only range.
3. Battery & Range
Specification EV (Tesla Model 3) PHEV (Toyota RAV4 Prime) Hybrid (Toyota Camry Hybrid)
Battery Size 60-82 kWh (Tesla Model 3) 18.1 kWh 1.6 kWh
Range (combined) 272-358 miles 600+ miles (total with gas) 680 miles
EVs have significantly larger batteries, providing extended electric-only range but require charging infrastructure.
PHEVs offer a smaller electric range but combine the benefits of a battery and traditional fuel for long-distance travel.
Hybrids rely on small batteries for short bursts of electric assistance, with no substantial electric-only range.
4. Maintenance Cost/Year
Specification EV (Tesla Model 3) PHEV (Toyota RAV4 Prime) Hybrid (Toyota Camry Hybrid)
Estimated Annual Maintenance Cost $400-$600 $500-$700 $450-$600
EVs have lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts (no engine oil changes, fewer fluids, less brake wear).
PHEVs have moderately higher maintenance costs due to the complexity of both electric and gasoline systems.
Hybrids are generally less expensive than PHEVs but more than EVs due to their reliance on gasoline engines.
5. Trunk Size
Specification EV (Tesla Model 3) PHEV (Toyota RAV4 Prime) Hybrid (Toyota Camry Hybrid)
Trunk Space 15 cu ft (plus front trunk) 33.5 cu ft 15.1 cu ft
Max Cargo Space 22.9 cu ft (w/ rear seats folded) 63.2 cu ft N/A
EVs often benefit from having both a front and rear trunk (as in Tesla models).
PHEVs, especially SUVs like the RAV4 Prime, offer more cargo capacity than hybrids or sedans.
Hybrids offer similar trunk space to their gas-powered counterparts.
6. Defects/Type Issues
EVs (Tesla):
Tesla vehicles have experienced build quality issues in earlier models, including panel gaps and paint quality concerns. However, Tesla’s software and battery systems are generally reliable.
PHEVs (Toyota):
Toyota RAV4 Prime has few major issues but may experience software glitches related to the transition between electric and gasoline modes.
Hybrids (Toyota):
Toyota hybrids like the Camry Hybrid have a long-standing reputation for reliability. However, minor issues such as infotainment bugs have been reported.
Conclusion:
EVs (e.g., Tesla Model 3) are best for those who can rely on charging infrastructure and prefer lower running costs with a focus on eco-friendly driving.
PHEVs (e.g., Toyota RAV4 Prime) offer the best of both worlds, with electric-only driving for short trips and gasoline for longer journeys, making them more versatile.
Hybrids (e.g., Toyota Camry Hybrid) are ideal if you want high fuel efficiency without the need for charging, offering a balance between cost, reliability, and convenience.
Youtube
